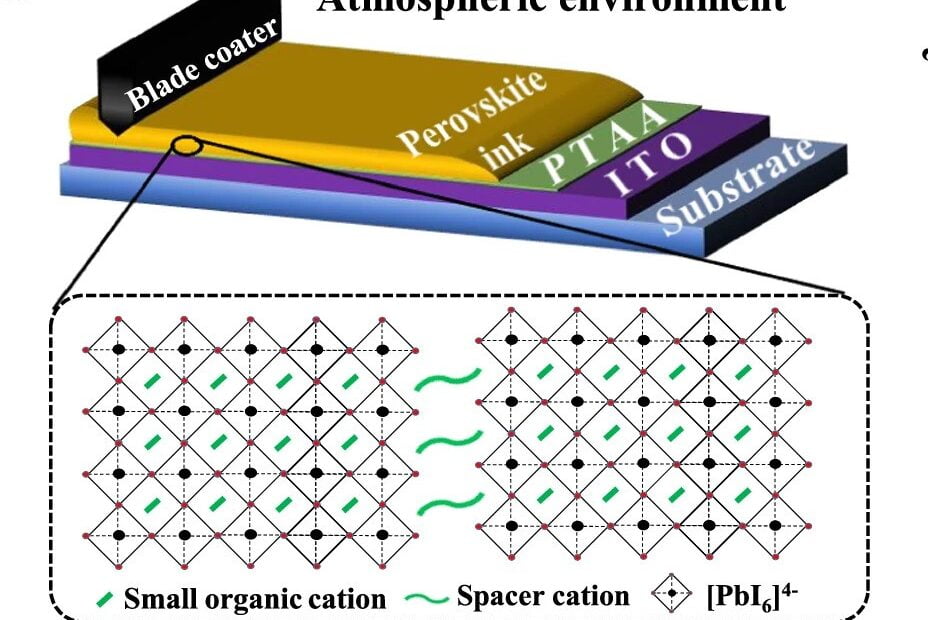
Chinese researchers claim to have developed an “ultrastable” perovskite solar cell based on a two-dimensional, Dion-Jacobson phase perovskite. The device was constructed with blade coating technology and is scalable, according to its creators.
July 29, 2024 Lior Kahana
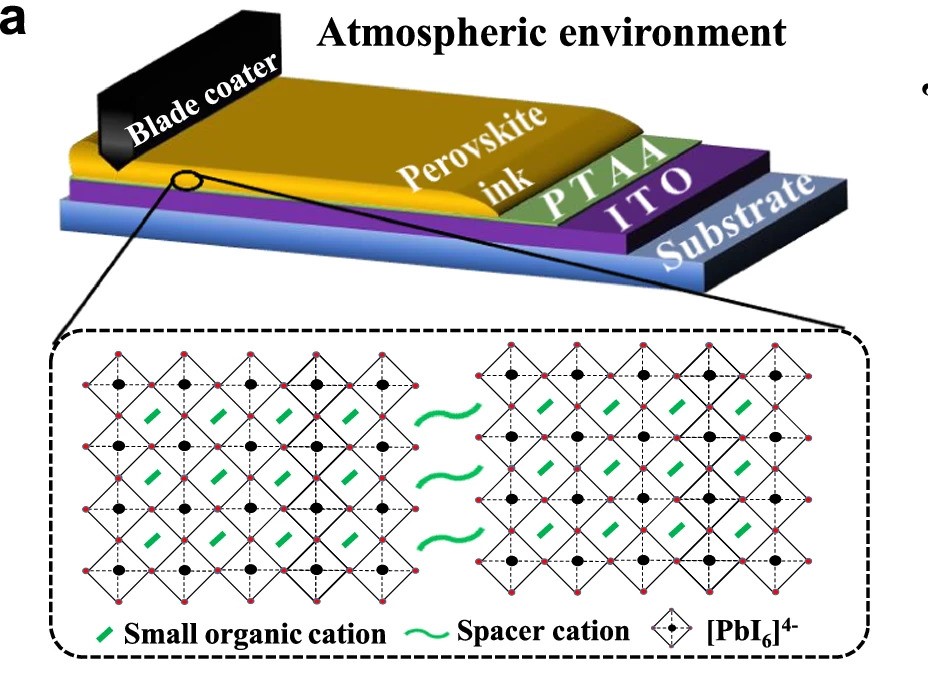
Illustration of the blade-coating film and the device configuration
Image: National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, CC BY 4.0
Share
Researchers led by China’s National Center for Nanoscience and Technology have developed a 2D Dion-Jacobson (DJ) perovskite solar cell that reportedly shows high stability levels while achieving a power conversion efficiency of 19.11%.
Two-dimensional (2D) Dion-Jacobson (DJ) phase perovskites have sparked interest in the scientific community due to their stability against harsh environmental conditions and their competitive performance in optoelectronic applications. Solar cells based on DJ perovskites, however, have shown comparatively poor performance compared to their 3D counterparts.
For its cell, the Chinese group utilized a perovskite material known as (CDMA)(MA)n−1PbnI3n+1, where CDMA stands for 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanammonium. “Structural analyses show that these materials have an extraordinarily slight interlayer-displacement quantum-well configuration that differs from most DJ perovskites, which can reduce interlayer spaces and tune their mutual alignment to facilitate interlayer charge transport and structural stability,” explained the researchers.
The device was constructed with blade coating technology and is scalable, according to the academics. It was built with a substrate made of glass and indium tin oxide (ITO), a hole transport layer (HTL) based on poly[bis(4-phenyl)(2,5,6-trimethylphenyl)amine (PTAA), CDMA-based DJ perovskite layer, a buckminsterfullerene (C60) electron transport layer (ETL), a bathocuproine (BCP) buffer layer, and a top electrode made of silver (Ag).
For reference, the group also created a similar cell with a change in the DJ perovskite layer. Whereas the novel structure was based on CDMA, the reference cell was based on PDMA, which stands for 1,4-phenylenedimethanammonium. PDMA DJ has a similar organic molecular configuration to CDMA materials, but they have been more widely studied.
Tested under standard illumination conditions, the CDMA DJ cell achieved an efficiency of 19.11%, an open-circuit voltage of 1.16 V, a short-circuit current density of 20.41 mA cm−2, and a fill factor of 80.56%. The reference PDMA DJ device obtained an efficiency of 14.87%, an open-circuit voltage of 1.06 V, a short-circuit current density of 18.32 mA cm−2, and a fill factor of 76.46%.
“Importantly, fabricated cells also exhibit remarkable humidity, thermal, and operational stability,” highlighted the group. “After keeping them in a 90% relative humidity (RH) or 85 C continuous aging condition for over 4000 h and 5000 h, respectively, the devices show an 8% degradation for the humidity stability test and negligible efficiency loss for thermal stability measurement. Particularly, the operational stability under continuous light stress shows negligible efficiency loss exceeding 6000 h.”
Concluding the article, the scientists added that “the designed interlayer-displacement DJ series provides a significant and potential pathway for constructing new structurally stable 2D perovskites. The blade-coating application of the designed DJ perovskite solar cells might spur new developments in scalable technology and their commercialization process.”
The new cell architecture were introduced in “Ultrastable and efficient slight-interlayerdisplacement 2D Dion-Jacobson perovskite solar cells,” published in Nature Communications. The research team included scientists from China’s National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, the University of South China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Beijing Technology And Business University, and the Beihang University.